GALIC – Code
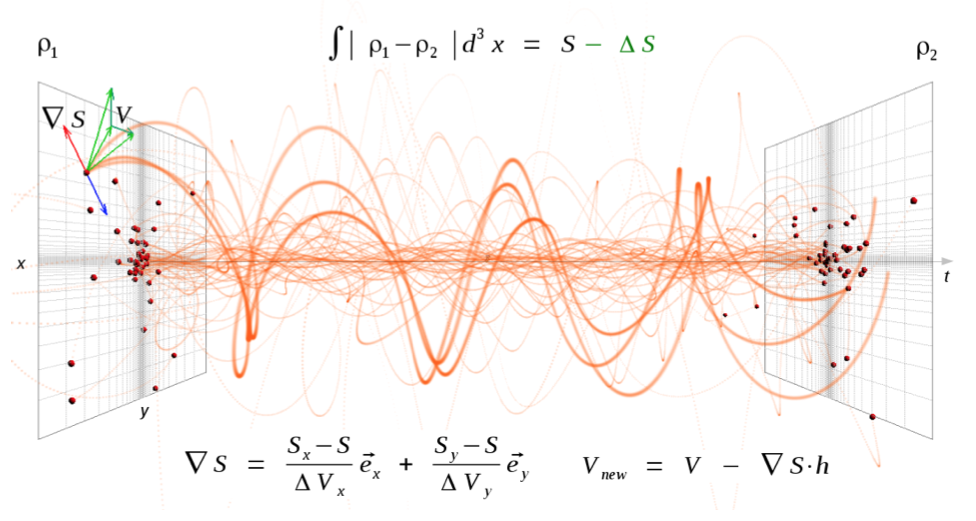
The GALIC code is a publicly available program that implements a new iterative method for the construction of N-body galaxy models in collisionless equilibrium. The method uses elements of Schwarzschild’s technique and of the made-to-measure method, but is based on a different principle. Starting with some initial assignment of particle velocities, the difference of the time-averaged density response produced by the particle orbits with respect to the initial density configuration is characterized through a merit function, and a stationary solution of the collisionless Boltzmann equation is found by minimizing this merit function directly by iteratively adjusting the initial velocities. Because the distribution function is in general not unique for a given density structure, the merit function is augmented with additional constraints that single out a desired target solution. The velocity adjustment is carried out with a stochastic process in which new velocities are randomly drawn from an approximate solution of the distribution function, but are kept only when they improve the fit. The method converges rapidly and is flexible enough to allow the construction of solutions with third integrals of motion, including disc galaxies in which radial and vertical dispersions are different.
The method has been developed by Denis Yurin as part of this PhD thesis supervised by Volker Springel. The code can be downloaded as
galic.tar.gz (version 1.0)
which contains the source code as well as a README file with instructions for building and running the code. We note that the code is parallelized for distributed memory based on MPI.
The principal reference for the method and the code is the paper:
- An iterative method for the construction of N-body galaxy models in collisionless equilibrium
Yurin D., Springel V. (2014)
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 444, 62 [ADS]
Über das HITS
Das HITS (Heidelberger Institut für Theoretische Studien) wurde 2010 von dem Physiker und SAP-Mitbegründer Klaus Tschira (1940-2015) und der Klaus Tschira Stiftung als privates, gemeinnütziges Forschungsinstitut gegründet. Es betreibt Grundlagenforschung in den Naturwissenschaften, der Mathematik und der Informatik. Zu den Hauptforschungsrichtungen zählen komplexe Simulationen auf verschiedenen Skalen, Datenwissenschaft und -analyse sowie die Entwicklung rechnergestützter Tools für die Forschung. Die Anwendungsfelder reichen von der Molekularbiologie bis zur Astrophysik. Ein wesentliches Merkmal des Instituts ist die Interdisziplinarität, die in zahlreichen gruppen- und disziplinübergreifenden Projekten umgesetzt wird. Die Grundfinanzierung des HITS wird von der Klaus Tschira Stiftung bereitgestellt.